What Is Electro
Deionisation and How Does It Work?
Electro deionisation, often referred to as EDI, is an advanced water purification technology used to produce consistently high purity water for industrial and process-critical applications. It is most commonly installed downstream of reverse osmosis systems and is widely used in sectors where even trace levels of dissolved ions can affect performance, compliance, or product quality.
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, power generation, electronics manufacturing, laboratories, and hydrogen production all rely on high purity water as a core process input. In these environments, water quality must be stable, predictable, and tightly controlled. Electro deionisation plays a key role in achieving this by polishing pre-treated water to extremely low conductivity levels on a continuous basis.
Unlike traditional deionisation methods that rely on chemical regeneration, electro deionisation uses a combination of ion exchange resins, selective membranes, and an electrical field to remove ionic contaminants continuously. This removes the need for acids and alkalis while delivering a reliable and repeatable water quality output when the system is properly designed and operated.
Understanding how electro deionisation works, where it fits within a complete water treatment system, and what its limitations are is essential when specifying pure water solutions for industrial use.
Why You Can Trust Us
AllWater Technologies designs and supports electro deionisation systems as part of fully engineered pure water solutions. With decades of experience across industrial sectors, the team understands the chemistry, materials, and operational realities behind EDI, ensuring systems are specified correctly and perform reliably long term.
What Is Electro Deionisation?
Electro deionisation is a polishing technology designed to remove residual dissolved ionic species from water following primary treatment. In most cases, this primary treatment is reverse osmosis, which removes the majority of total dissolved solids before the water enters the EDI system.
The purpose of electro deionisation is not bulk salt removal but refinement. It targets low level ionic contaminants that remain after reverse osmosis and reduces them to extremely low concentrations. Under the right conditions, EDI systems can consistently produce water with resistivity values approaching 18.2 MΩ·cm, which is considered ultra-pure water.
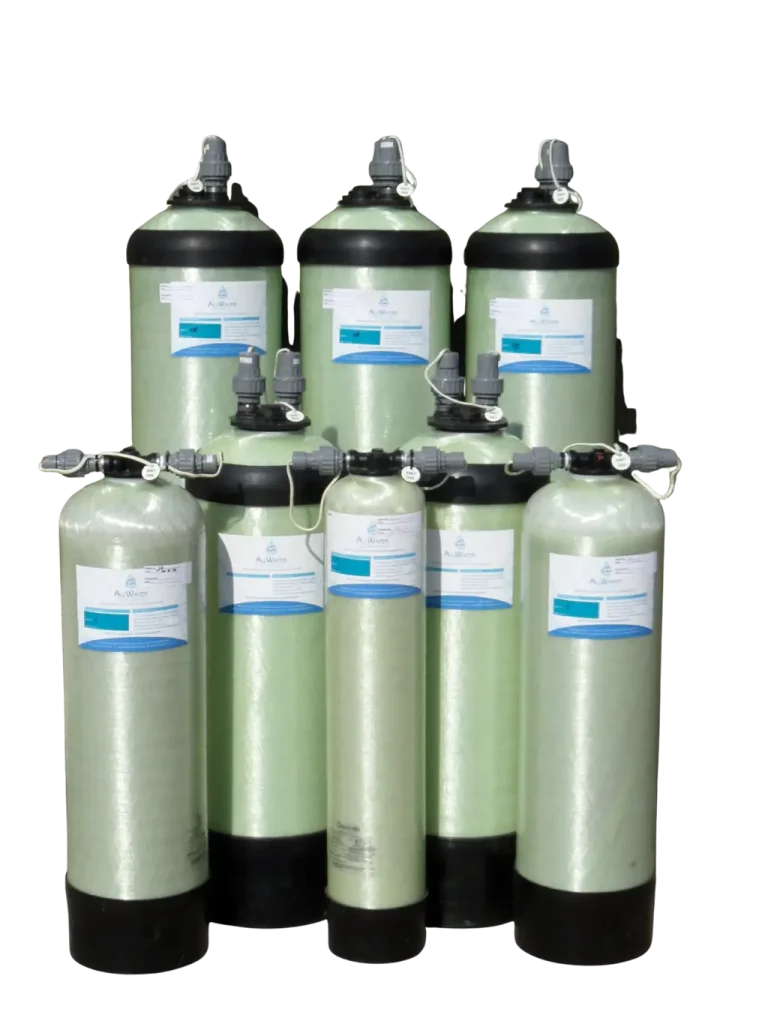
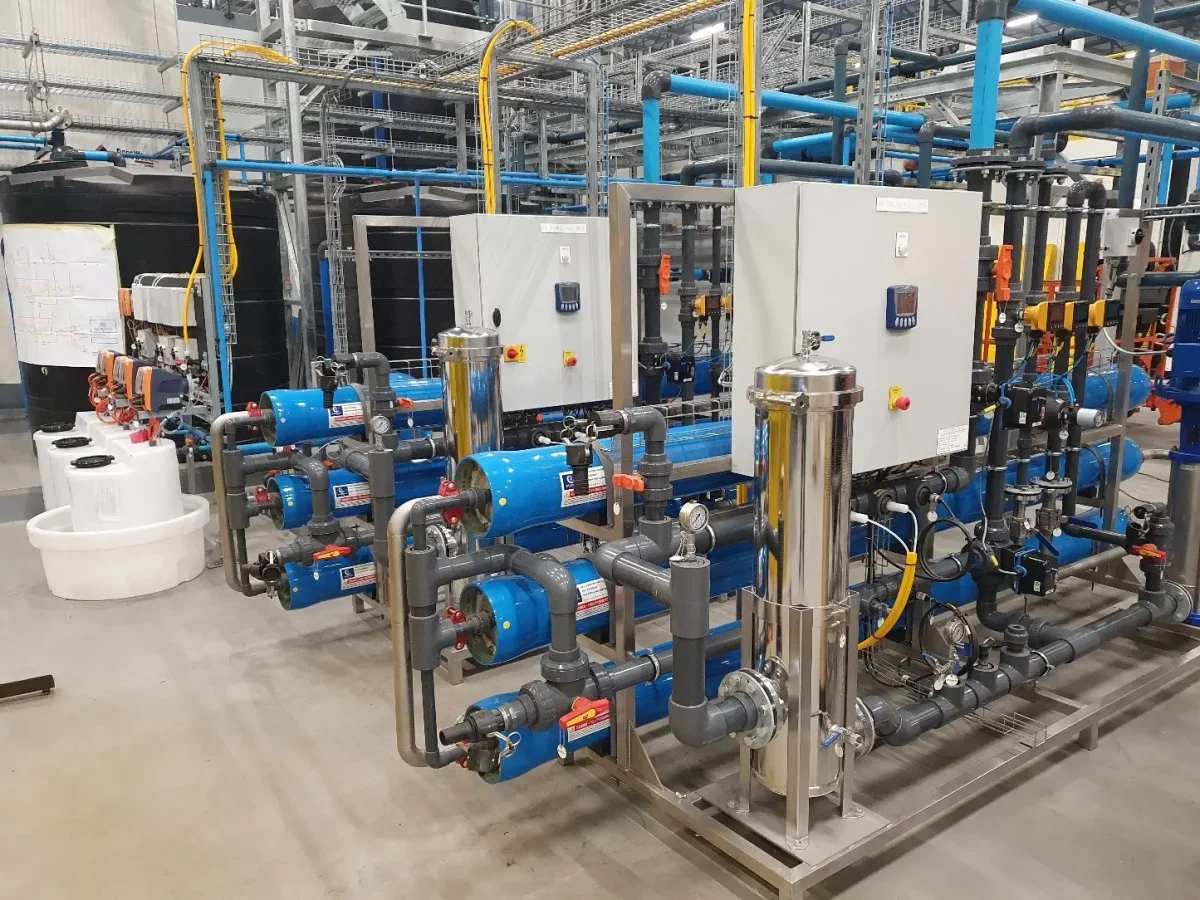
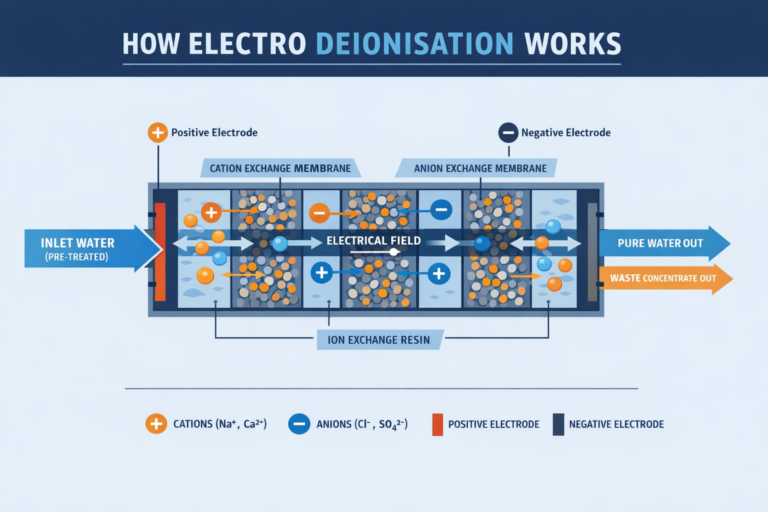
An EDI system combines three fundamental elements:
- ion exchange resins that temporarily capture charged ions
- ion selective membranes that allow specific ions to pass while blocking others
- a direct current electrical field that drives ion migration and resin regeneration
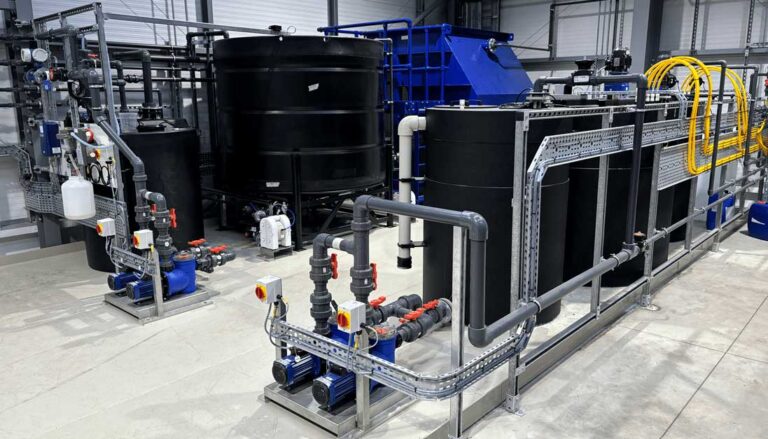
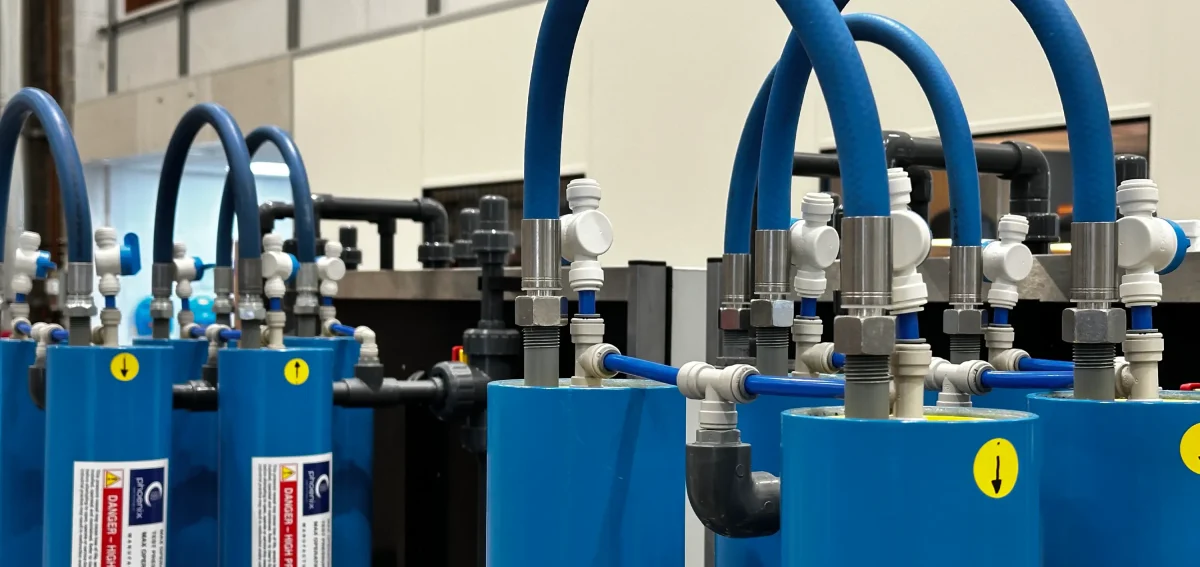
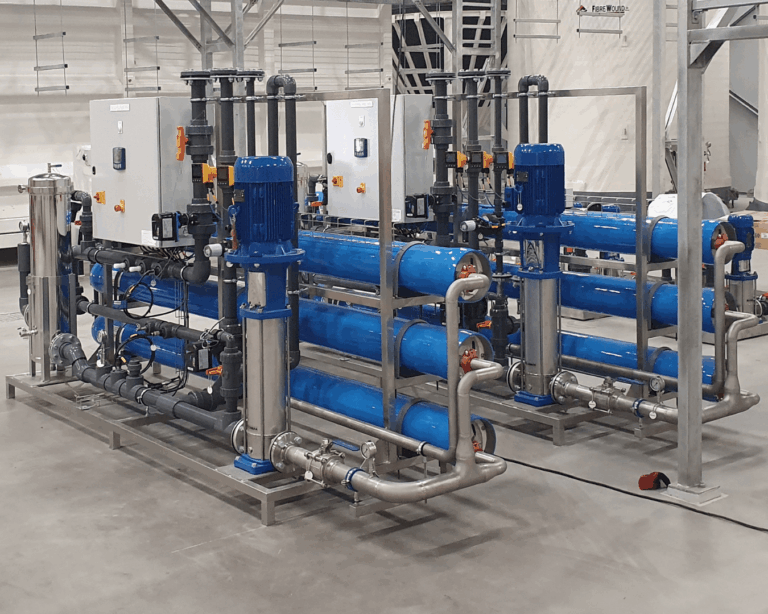
These components are arranged within modular EDI stacks that allow water to flow continuously through the system. Because the resins are regenerated electrically rather than chemically, the process does not require periodic shutdowns or chemical dosing cycles.
This continuous operation is one of the defining characteristics of electro deionisation and a key reason it is favoured in applications that demand stable water quality around the clock.
How Electro Deionisation Works
To understand how electro deionisation works, it is useful to break the process down into stages.
Pre-treated water enters the EDI module after passing through upstream treatment stages. This water is typically low in hardness, low in silica, and has a greatly reduced ionic load thanks to reverse osmosis.
Inside the EDI module, the water flows through compartments filled with mixed bed ion exchange resin. As the water passes through these compartments, dissolved ions such as sodium, chloride, calcium, magnesium, sulphate, and nitrate are attracted to and held by the resin beads.
At the same time, a direct current electrical field is applied across the module. This electrical field causes the captured ions to migrate off the resin and move through adjacent ion selective membranes. Positively charged ions move toward the cathode, while negatively charged ions move toward the anode.
These ions are directed into concentrate channels, where they are flushed away from the system as a controlled waste stream. Meanwhile, the purified water continues through the product channels and exits the module with a significantly reduced ionic content.
Crucially, the electrical field continuously regenerates the ion exchange resin in situ. This means the resin does not become exhausted in the same way as conventional mixed bed systems, removing the need for chemical regeneration using acid and caustic solutions.
The result is a steady, continuous supply of high purity water with minimal operator intervention.
Why Reverse Osmosis Is Essential Before EDI
Electro deionisation is highly effective, but it is not designed to treat raw water directly. The technology relies on a high quality feed water to operate reliably and efficiently.
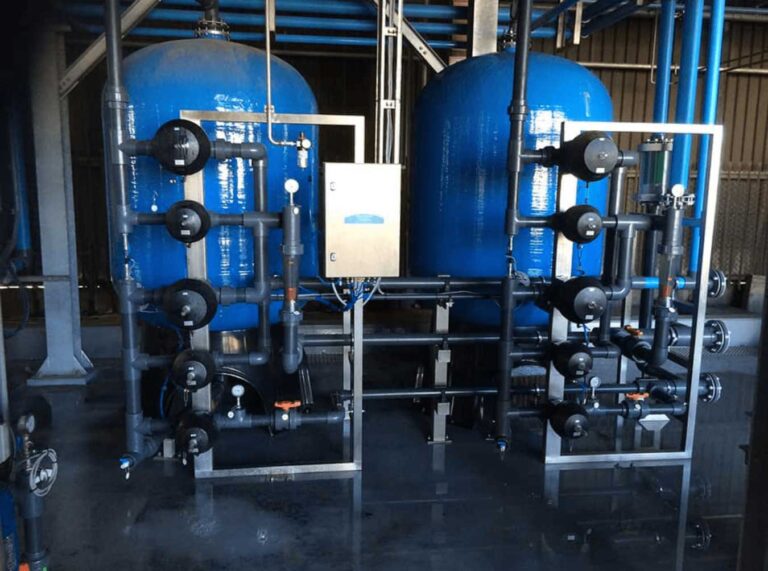
Reverse osmosis is almost always used upstream of EDI to remove the majority of dissolved salts, organic compounds, bacteria, and particulates. By significantly reducing the total dissolved solids entering the EDI system, reverse osmosis protects the ion exchange resin and membranes from fouling, scaling, and premature failure.
Without adequate pre-treatment, EDI modules can suffer from unstable performance, reduced water quality, and shortened component life. High hardness levels, elevated silica, or excessive carbon dioxide can all compromise EDI operation if they are not addressed at the design stage.
This is why electro deionisation should never be considered in isolation. It must be integrated into a properly engineered treatment train that may include multimedia filtration, carbon filtration, water softening, degassing, and reverse osmosis depending on the incoming water quality and application requirements.
Typical Applications of Electro Deionisation
Electro deionisation is used in applications where consistent high purity water is essential and where chemical regeneration presents operational, safety, or environmental challenges.
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, EDI is commonly used to produce purified water for formulation, cleaning, and clean-in-place systems. Consistent water quality is critical to meeting regulatory standards and maintaining batch integrity.
In power generation, electro deionisation is used to polish boiler feed water and turbine make-up water. Even trace ionic contamination can contribute to corrosion, scaling, or stress cracking in high pressure systems.
Electronics and semiconductor manufacturing rely on ultra-pure water for rinsing and processing sensitive components, where any ionic residue can cause defects or performance issues.
Laboratories and analytical facilities use EDI to produce high purity water for testing, sample preparation, and equipment feed.
Emerging applications such as hydrogen production also require extremely pure feed water to protect electrolysers and maintain efficiency over time.
EDI Water Quality and Material Compatibility
While high purity water is often described as clean or pure, it is important to understand that water produced by electro deionisation is chemically aggressive if not properly managed.
Water with very low ionic content has a strong tendency to dissolve materials it comes into contact with. Fully deionised water can attack metals such as copper and mild steel, particularly if system materials are not selected correctly or if water chemistry is not stabilised.
This makes material compatibility a critical consideration when designing EDI systems. Pipework, storage tanks, valves, and fittings must be chosen to withstand ultra-pure water without leaching contaminants or suffering corrosion.
Stainless steel grades, suitable polymers, and specialist materials are commonly used downstream of EDI systems. System design must also consider flow velocities, temperature, and stagnation risks.
This is one of the key reasons why electro deionisation systems should only be specified and installed by experienced water treatment engineers with a thorough understanding of both water chemistry and mechanical design.
Advantages of Electro Deionisation
When applied correctly, electro deionisation offers several clear advantages over traditional deionisation methods.
The most significant benefit is continuous operation. EDI systems produce high purity water without the need for shutdowns, regeneration cycles, or resin changeouts associated with conventional mixed bed systems.
The elimination of acid and caustic chemicals reduces health and safety risks, simplifies site compliance, and lowers environmental impact. It also removes the need for chemical storage, handling, and waste neutralisation.
Water quality is stable and predictable, which is critical for process consistency and regulatory compliance. Automation and monitoring allow performance to be tracked in real time.
Over the long term, EDI systems can offer lower operating costs, particularly in applications with continuous demand for high purity water.
Limitations and Design Considerations
Despite its advantages, electro deionisation is not suitable for every application.
EDI systems are sensitive to feed water quality and operating conditions. Elevated carbon dioxide can reduce resistivity performance. Silica can pass through membranes if not controlled upstream. Hardness breakthrough can lead to scaling and irreversible damage.
Electrical supply stability, correct flow rates, and appropriate control strategies are also essential. EDI is a precision technology and does not tolerate poor design or neglect.
In some applications, conventional mixed bed deionisation may still be more appropriate, particularly where demand is intermittent or feed water quality is highly variable.
A detailed water analysis and process review is always required before selecting electro deionisation.
AllWater Technologies provides electro deionisation as part of fully integrated pure water treatment solutions rather than as standalone equipment.
The process begins with a detailed assessment of raw water quality, required product water specification, flow rates, and operational constraints. This allows the treatment system to be engineered correctly from the outset.
AllWater designs complete systems that may include filtration, softening, reverse osmosis, degassing, electro deionisation, storage, and distribution. Each element is selected to protect downstream equipment and ensure stable long-term performance.
Installation is carried out with careful attention to materials, controls, and commissioning procedures. Performance is verified against design criteria, and operators are supported with training and documentation.
Ongoing service support includes maintenance, fault diagnosis, consumables supply, and system optimisation. This ensures electro deionisation systems continue to operate reliably throughout their lifecycle.
Click here for more information about our Electro-Deionisation Systems
Electro deionisation is a powerful and efficient technology when applied correctly. It offers a reliable route to high purity water without the operational burden of chemical regeneration.
Success depends on correct system design, appropriate pre-treatment, material compatibility, and experienced support. When these factors are addressed, EDI can deliver long-term performance, reduced risk, and consistent water quality for demanding industrial applications.
Get in Touch with AllWater Technologies
We’re here to help with all your water treatment needs. Whether you have questions about our services, want to discuss a project, or need support, our team is ready to assist you. Fill out the form for general enquiries, or you are welcome to email direct or give us a call.
AllWater House
Unit 2,
Cheddar Business Park,
Wedmore Road,
Cheddar
BS27 3EB
Opening hours
Mon-Fri: 08:30-17:30 (GMT)